|
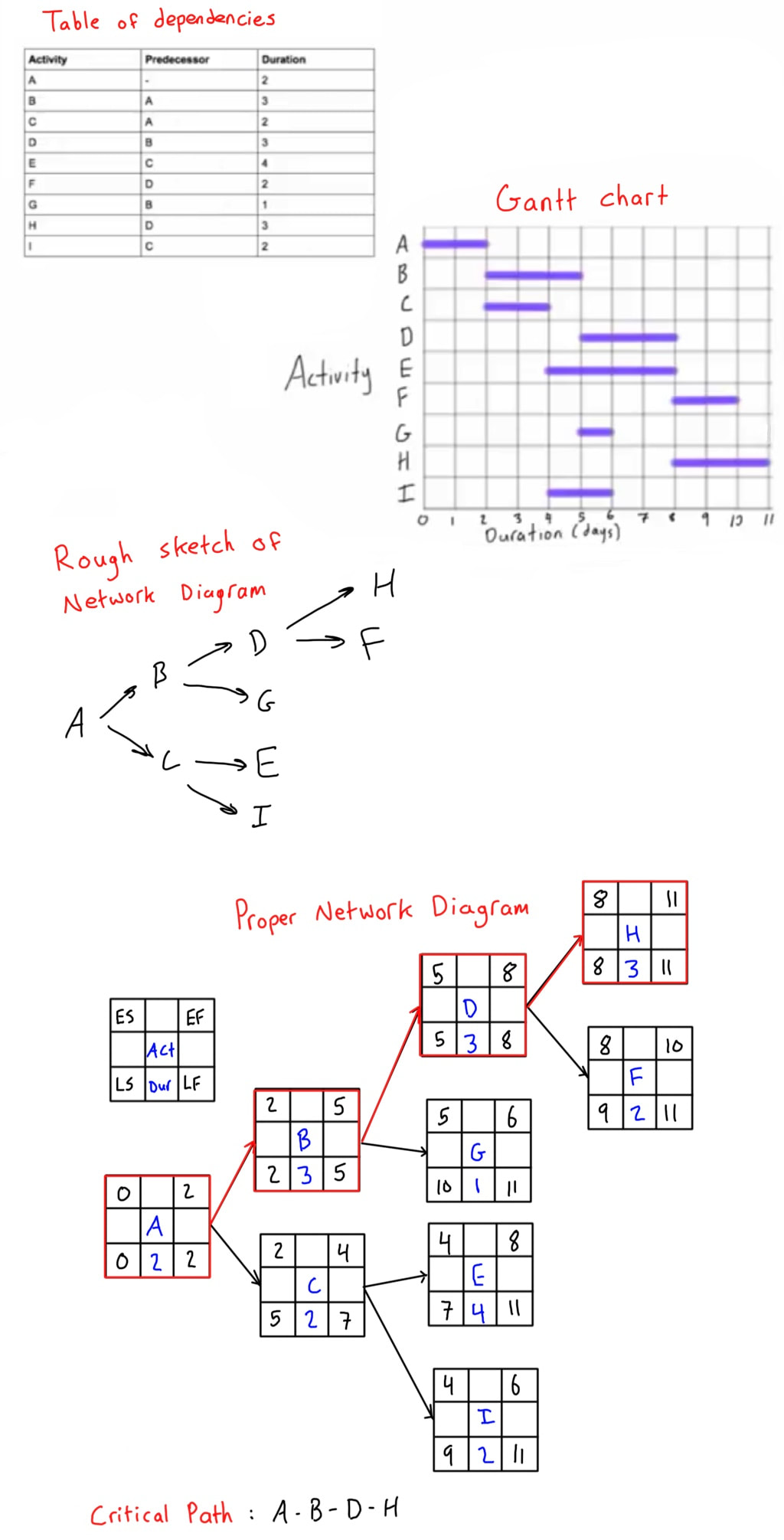
Below is the table of dependencies and Gantt from this Project Management Tutorial. The original tutorial did not include drawing the network diagram, so I have included it below for clarification. It is an AON (Activity on Arrow - also sometimes called Activity on Node) network diagram. When drawing a network diagram, it’s best to first draw a rough sketch based on the activity relationships. You might not get it right on the first attempt, but that’s fine, just erase and redraw until you have no (or the least amount possible) crossovers. Once your rough sketch is good, format it to be nicer like you see below. Start with either 0 or 1 (depends which numbering system you’re been taught to use), and then complete the forward pass. Notice that there are five terminal activities in this project. Find the one with the greatest EF (it’s 11), and then put that value as the LF for all terminal activities, then proceed with the backward pass. Quick note: If you draw your network diagram starting with a zero like I do, then you should also draw your Gantt chart starting with a zero. They should match! The beginning and end of each activity on the Gantt chart should also correspond to the ES (early start) and EF (early finish) of each activity. The critical path is made up of path of activities who’s ES and LS are the same (or EF and LF). Highlight it either on the diagram like I did in red, or write it below. The critical path of this project is A - B - D H. You can find the whole project management course here.
Comments are closed.
|
|
© Copyright www.engineer4free.com 2012 - 2024 All Rights Reserved
About | Course List | Patreon | Newsletter | Blog | ToS | Contact Engineer4Free is committed to sustainability. You should be too. |
|