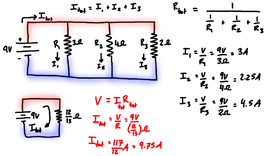
Comments are closed.
|
👋 Hello! I'm proud to offer all of my tutorials for free. If I have helped you then please support my work on Patreon:
Other ways to support Engineer4Free <3 I work hard to create Engineer4Free. Please support my work on Patreon. You can also: |
|
© Copyright www.engineer4free.com 2012 - 2024 All Rights Reserved
About | Course List | Patreon | Newsletter | Blog | ToS | Contact Engineer4Free is committed to sustainability. You should be too. |
|